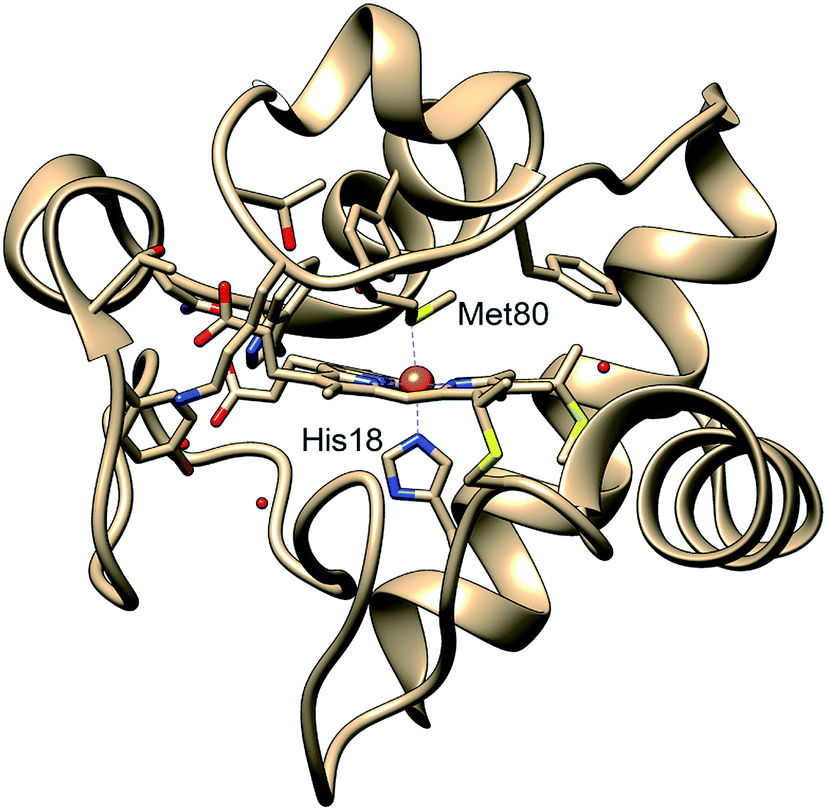
Cytochrome c (cyt c) is a model system for heme metalloprotein folding dynamics and chemical interactions. In this experiment, a denatured ground state carbon monoxide-, CO, bound cyt c is prepared, and its folding is subsequently triggered by the photolysis of CO from the iron center. A pulsed laser initiates the folding dynamics in less than 10 ns, and time-delayed x-ray pulses capture the structural information as small-/wide- angle x-ray scattering patterns. The scattering patterns taken before and after the photolysis event are subtracted to show the scattering difference plots below. The scattering difference signal plotted along the momentum transfer, q, is proportional to the change in characteristic lengthscales of the molecule.This interactive tool integrates the time series according to the brushing window to explore trends in the dataset (Hsu et al. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 9788-9800).